

Libros antiguos y modernos
Yeaple,HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC POWER AND CONTROL,McGraw-Hill,1966[idraulica
29,90 €
Modo Infoshop
(Bologna, Italia)
Los gastos de envío correctos se calculan una vez añadida la dirección de envío durante la creación del pedido. El vendedor puede elegir uno o varios métodos de envío: standard, express, economy o in store pick-up.
Condiciones de envío de la Librería:
Para los productos con un precio superior a 300 euros, es posible solicitar un plan de pago a plazos al Maremagnum. El pago puede efectuarse con Carta del Docente, Carta della cultura giovani e del merito, Administración Pública.
Los plazos de entrega se estiman en función de los plazos de envío de la librería y del transportista. En caso de retención aduanera, pueden producirse retrasos en la entrega. Los posibles gastos de aduana corren a cargo del destinatario.
Pulsa para saber másFormas de Pago
- PayPal
- Tarjeta de crédito
- Transferencia Bancaria
-
-
Descubre cómo utilizar
tu Carta del Docente -
Descubre cómo utilizar
tu Carta della cultura giovani e del merito
Detalles
Descripción
HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC POWER AND CONTROL
Design, performance, application
McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966
Copertina rigida, 29x22 cm, pp. 338
Contiene grafici, tabelle e disegni in bianco e nero
Peso: 1351 g.
Lingua inglese.
cod 7261
CONDIZIONI DEL LIBRO: la sovracopertina presenta degli strappi,
mentre l’interno è in condizioni perfette.
INDICE
Preface
Chapter 1. Fluid Properties—Oil, Synthetics, Air, and Gases 1
Modern Fluids for Power and Control: Introduction
3
What’s Hot in Fluids? For Temperatures from 400 to 850 F
8
High-pressure Air: Data to 12,000 psi
17
Chapter 2. Reservoirs and Containers—Design, Application,
Safety
21
Fluid-system Reservoir: Design and Performance
22
Oil-system Cooling: Simplified Calculations
24
Air Bubbles in Oil: A Three-pronged Attack
29
Pressurized Containers: Design, Selection, Safety
34
Chapter 3. Filters and Contaminants—Particle Size, Filter Selection
41
Measuring Fluid Contamination: Particles Smaller Than 40 microns
42
Evaluating Fluid-filtering Media: Nominal vs. Absolute Ratings
45
Chapter 4. Flexible Piping and Fittings—Hose, Couplings,
Joints, Manifolds
57
Standards for Metal Hose: Corrugated and Interlocked
58
Quick-connect Couplings Cut Costs: Representative Types, How They
Work
62
Swivel Joints: The Various Types, How They Work
66
Designing with Swivel Joints
70
Sandwich Manifolding: Eliminates Tubing and Fittings
73
Chapter 5. Flow and Pressure Drop—Equations, Measurements
75
Flow Resistance in Pipe: Summary of Equations for Fluid Friction
76
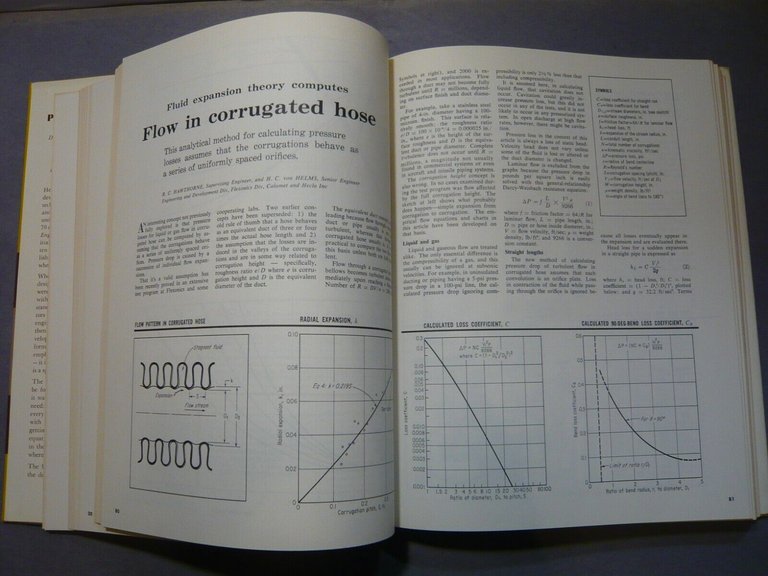
Flow in Corrugated Hose: New Fluid Expansion Theory
80
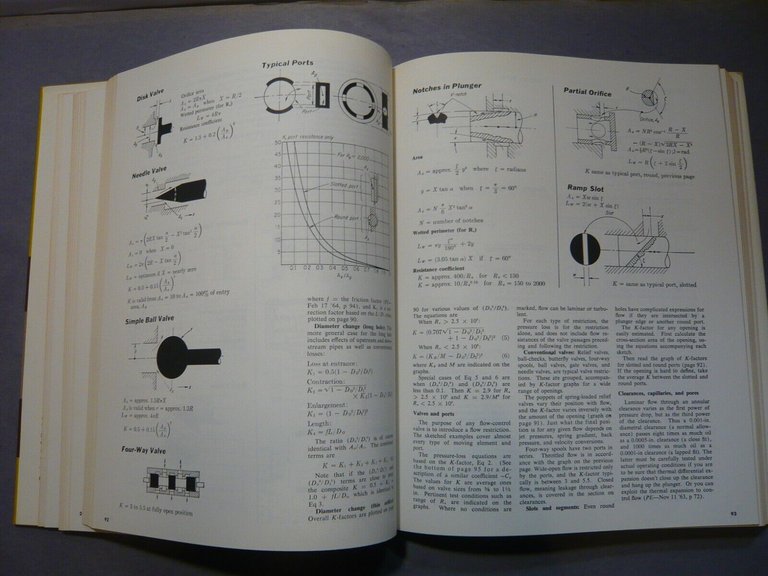
Local Resistance to Flow: Coefficients for All Fittings, Restrictions
83
Fluid Throttling Devices: For Intentional Flow Resistance
89
Close-clearance Orifices: For Flow Clearances in Thousandths
96
Errorless Orifices: Series and Parallel for Constant Discharge Coefficient
101
Airflow in Components: Graphical Solution of Flow Factor Equation
102
Which Air-flow Equation: Comparison of Ten Key Equations
112
How to Select a Flowmeter: Roundup of 16 Types
118
Chapter 6. Pumps, Compressors, and Blowers—Performance,
Application
129
Positive-displacement Pumps: Design and Performance of 17 Types
130
Cavitation in Positive-displacement Pumps: Simple Graphical Method
140
Squeegee Pump Performance: First Proven Application Technique
143
400-cycle Centrifugal Pump : Performance Compared with Regulars
151
Adiabatic Head Selects Air Compressor Type
155
Equations Find the Right Impeller: Fan Pressure and Flow Coefficients
160
Chapter 7. Valves and Controls—Construction, Performance,
Application
165
Fluid Amplifiers Go Commercial: 18 Typical Fluid Logic Devices
166
Relief Valves: Simple, Pilot-operated, Electric, and By-pass Types
169
Pressure Control Valves: Counterbalance, Sequence, Unloading, Reducing 177 Flow Control Valves:
Non-compensated, Compensated, Pilot Check
184
Directional Valves: Two-way, Three-way, Four-way, Diversion
190
Valve Circuits: Regenerative, Tandem, High-low
197
Hydraulic Servovalves: Simple Theory and Design of Basic Types
203
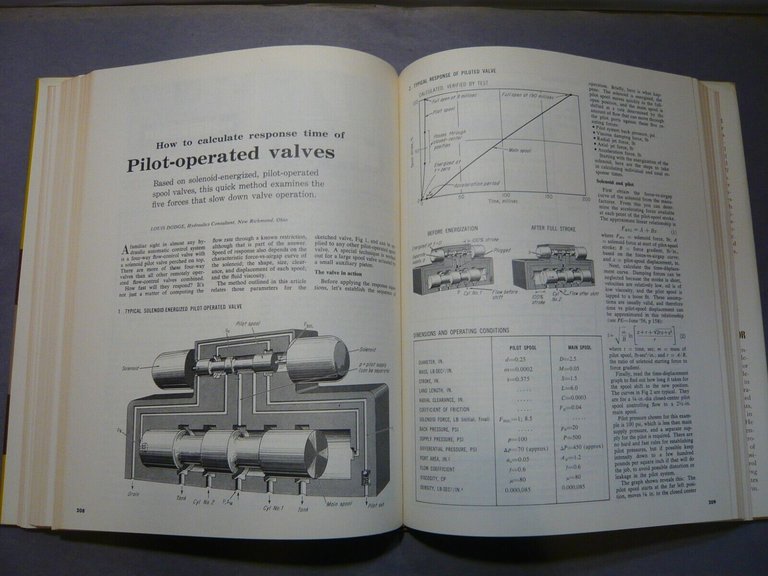
Pilot-operated Spool Valves: Calculation of Response Time
208
Ball Valves of Plastic: Ball, Plug, Globe, and Gate Types Compared
215
Manifold Control Valves: Five Manifolding Techniques
216
Chapter 8. Cylinders and Actuators—Stroke, Strength, Performance
223
Power Cylinder Mechanisms : Full-stroke
224
Power Cylinders: Intermediate Positions
226
Power Cylinders: Charts Give Safe Piston Rod Size
228
Six Fluid Power Force Amplifiers
230
When Pistons Need Brakes: Six Methods, Including Gearing
232
Regulate the Exhaust: Cushioning and Control of Air Cylinders
237
Chapter 9. Fluid Motors and Drives—Hydraulic, Pneumatic 239
Which Hydraulic Driver1 Hydrostatic, Hydrodynamic, Hydromechanical 241 Air Motors: Analysis and Design, Including Thermodynamics
255
Chapter 10. Dashpots, Damping, and Fluid Hammer
261
Dashpots and Damping: Practical Equations for All Problems
263
Liquid Springs: Design and Construction of Four Major Types
268
Design with Air Springs: Typical Application Has Adjustable Damping
271
Air snubbers Graphs: Shortcut Solution for Orifice Area. Pressure
272
Reduce Fluid Hammer: Theory and Design of Smoother Systems 276
Hydraulic Accumulators: Guide for Selection among Six Types 284
Chapter 11. Seals and Gaskets-Dynamic and Static Sealing 291
How to choose a dynamic Seal: Shaft, Face, Compression, Labyrinth 292
Labyrinth Shaft Seals: Leakage Equations for Non-contracting Seals 305
Bolted Gaskets: How to Select and apply the right gasket material 310
Chapter 12. System Performance—Flow Theory, Optimization, Reliability
315
Theory of Hydraulic Flow Control: Series
and Parallel Circuits
316
Split the Flow and Not the Pump: Designing Central Hydraulic Systems 332
Index
337

