

Rare and modern books
Yeaple,HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC POWER AND CONTROL,McGraw-Hill,1966[idraulica
29.90 €
Modo Infoshop
(Bologna, Italy)
The correct shipping costs are calculated once the shipping address is entered during order creation. One or more delivery methods are available at the Seller's own discretion: Standard, Express, Economy, In-store pick-up.
Bookshop shipping conditions:
For items priced over €300, it is possible to request an instalment plan from Maremagnum. Payment can be made with Carta del Docente, Carta della cultura giovani e del merito, Public Administration.
Delivery time is estimated according to the shipping time of the bookshop and the courier. In case of customs detention, delivery delays may occur. Any customs duties are charged to the recipient.
For more infoPayment methods
- PayPal
- Credit card
- Bank transfer
-
-
Find out how to use
your Carta del Docente -
Find out how to use
your Carta della cultura giovani e del merito
Details
Description
HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC POWER AND CONTROL
Design, performance, application
McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966
Copertina rigida, 29x22 cm, pp. 338
Contiene grafici, tabelle e disegni in bianco e nero
Peso: 1351 g.
Lingua inglese.
cod 7261
CONDIZIONI DEL LIBRO: la sovracopertina presenta degli strappi,
mentre l’interno è in condizioni perfette.
INDICE
Preface
Chapter 1. Fluid Properties—Oil, Synthetics, Air, and Gases 1
Modern Fluids for Power and Control: Introduction
3
What’s Hot in Fluids? For Temperatures from 400 to 850 F
8
High-pressure Air: Data to 12,000 psi
17
Chapter 2. Reservoirs and Containers—Design, Application,
Safety
21
Fluid-system Reservoir: Design and Performance
22
Oil-system Cooling: Simplified Calculations
24
Air Bubbles in Oil: A Three-pronged Attack
29
Pressurized Containers: Design, Selection, Safety
34
Chapter 3. Filters and Contaminants—Particle Size, Filter Selection
41
Measuring Fluid Contamination: Particles Smaller Than 40 microns
42
Evaluating Fluid-filtering Media: Nominal vs. Absolute Ratings
45
Chapter 4. Flexible Piping and Fittings—Hose, Couplings,
Joints, Manifolds
57
Standards for Metal Hose: Corrugated and Interlocked
58
Quick-connect Couplings Cut Costs: Representative Types, How They
Work
62
Swivel Joints: The Various Types, How They Work
66
Designing with Swivel Joints
70
Sandwich Manifolding: Eliminates Tubing and Fittings
73
Chapter 5. Flow and Pressure Drop—Equations, Measurements
75
Flow Resistance in Pipe: Summary of Equations for Fluid Friction
76
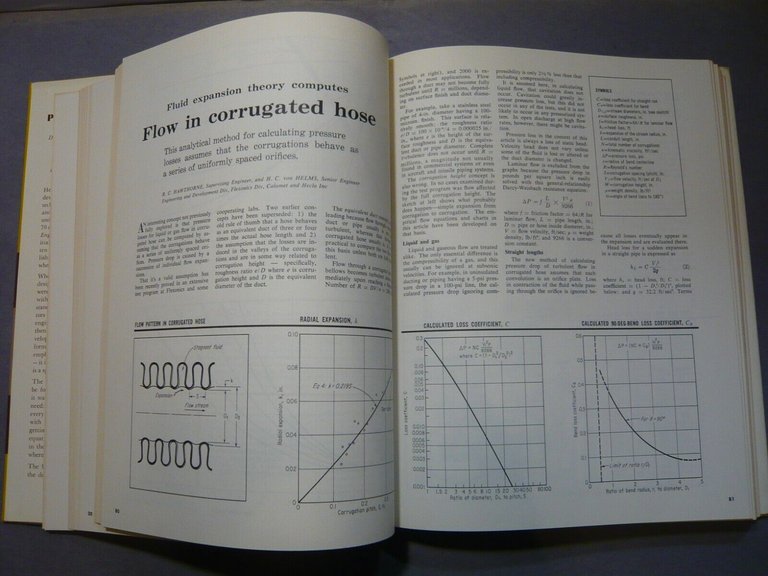
Flow in Corrugated Hose: New Fluid Expansion Theory
80
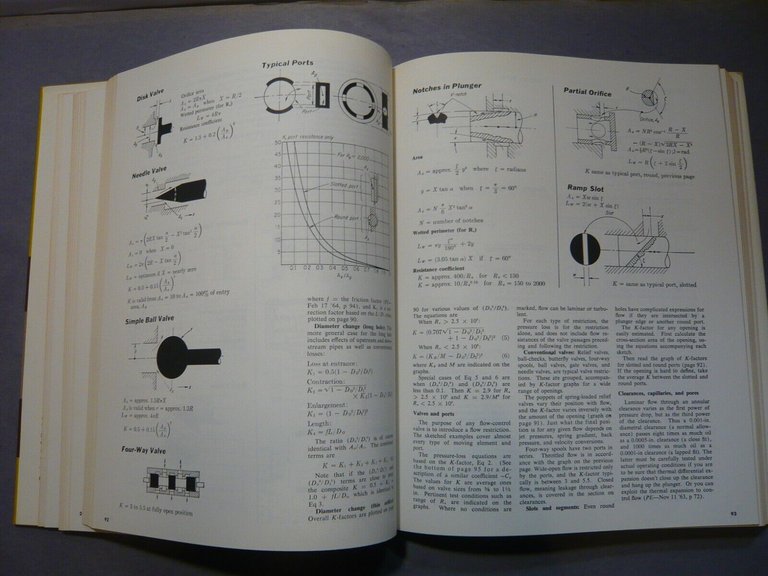
Local Resistance to Flow: Coefficients for All Fittings, Restrictions
83
Fluid Throttling Devices: For Intentional Flow Resistance
89
Close-clearance Orifices: For Flow Clearances in Thousandths
96
Errorless Orifices: Series and Parallel for Constant Discharge Coefficient
101
Airflow in Components: Graphical Solution of Flow Factor Equation
102
Which Air-flow Equation: Comparison of Ten Key Equations
112
How to Select a Flowmeter: Roundup of 16 Types
118
Chapter 6. Pumps, Compressors, and Blowers—Performance,
Application
129
Positive-displacement Pumps: Design and Performance of 17 Types
130
Cavitation in Positive-displacement Pumps: Simple Graphical Method
140
Squeegee Pump Performance: First Proven Application Technique
143
400-cycle Centrifugal Pump : Performance Compared with Regulars
151
Adiabatic Head Selects Air Compressor Type
155
Equations Find the Right Impeller: Fan Pressure and Flow Coefficients
160
Chapter 7. Valves and Controls—Construction, Performance,
Application
165
Fluid Amplifiers Go Commercial: 18 Typical Fluid Logic Devices
166
Relief Valves: Simple, Pilot-operated, Electric, and By-pass Types
169
Pressure Control Valves: Counterbalance, Sequence, Unloading, Reducing 177 Flow Control Valves:
Non-compensated, Compensated, Pilot Check
184
Directional Valves: Two-way, Three-way, Four-way, Diversion
190
Valve Circuits: Regenerative, Tandem, High-low
197
Hydraulic Servovalves: Simple Theory and Design of Basic Types
203
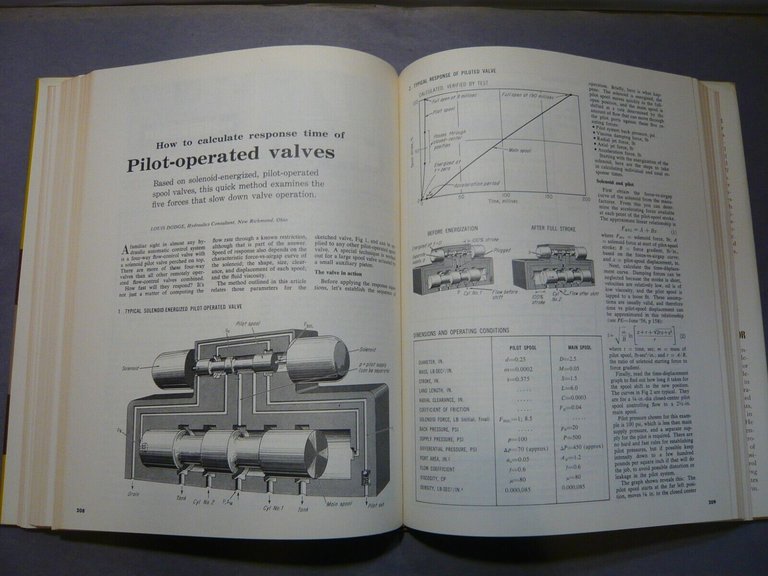
Pilot-operated Spool Valves: Calculation of Response Time
208
Ball Valves of Plastic: Ball, Plug, Globe, and Gate Types Compared
215
Manifold Control Valves: Five Manifolding Techniques
216
Chapter 8. Cylinders and Actuators—Stroke, Strength, Performance
223
Power Cylinder Mechanisms : Full-stroke
224
Power Cylinders: Intermediate Positions
226
Power Cylinders: Charts Give Safe Piston Rod Size
228
Six Fluid Power Force Amplifiers
230
When Pistons Need Brakes: Six Methods, Including Gearing
232
Regulate the Exhaust: Cushioning and Control of Air Cylinders
237
Chapter 9. Fluid Motors and Drives—Hydraulic, Pneumatic 239
Which Hydraulic Driver1 Hydrostatic, Hydrodynamic, Hydromechanical 241 Air Motors: Analysis and Design, Including Thermodynamics
255
Chapter 10. Dashpots, Damping, and Fluid Hammer
261
Dashpots and Damping: Practical Equations for All Problems
263
Liquid Springs: Design and Construction of Four Major Types
268
Design with Air Springs: Typical Application Has Adjustable Damping
271
Air snubbers Graphs: Shortcut Solution for Orifice Area. Pressure
272
Reduce Fluid Hammer: Theory and Design of Smoother Systems 276
Hydraulic Accumulators: Guide for Selection among Six Types 284
Chapter 11. Seals and Gaskets-Dynamic and Static Sealing 291
How to choose a dynamic Seal: Shaft, Face, Compression, Labyrinth 292
Labyrinth Shaft Seals: Leakage Equations for Non-contracting Seals 305
Bolted Gaskets: How to Select and apply the right gasket material 310
Chapter 12. System Performance—Flow Theory, Optimization, Reliability
315
Theory of Hydraulic Flow Control: Series
and Parallel Circuits
316
Split the Flow and Not the Pump: Designing Central Hydraulic Systems 332
Index
337

